WHAT IS HERD IMMUNITY - 356
WHAT IS HERD IMMUNITY
From time to time , we come across terms which sound highly scientific and rather difficult to understand . There is almost a deluge of such terms during recent times in these difficult days . PANDEMIC , EPIDEMIC, CONTAGIOUS HYDRXYCHLOROQUIN , REMDESIVIR AND THE LATEST TO JOIN THE LIST BEING
HERD IMMUNITY
Being just about Passable in my English and far from being Versatile in Tamizh , my offhand translation to AATTU MANTHAI PAZHAKKAM , somehow does not seem to have a connect with the issue on hand .
Here is where , our saviour at all such difficult times Mr Google or should it be Miss Google comes to help via their Wikipedia .
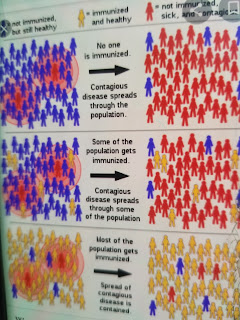
Herd immunity
Herd immunity (also called herd effect, community immunity, population immunity, or mass immunity) is a form of indirect protection from infectious disease that can occur with some diseases when a sufficient percentage of a population has become immune to an infection, whether through vaccination or previous infections,[1] thereby reducing the likelihood of infection for individuals who lack immunity.[2][3][4] Immune individuals are unlikely to contribute to disease transmission, disrupting chains of infection, which stops or slows the spread of disease.[5] The greater the proportion of immune individuals in a community, the smaller the probability that non-immune individuals will come into contact with an infectious individual.[2]

Individuals can become immune by recovering from an earlier infection or through vaccination.[5] Some individuals cannot become immune because of medical conditions, such as an immunodeficiency or immunosuppression, and for this group herd immunity is a crucial method of protection.[6][7] Once the herd immunity threshold has been reached, disease gradually disappears from a population.[7] This elimination, if achieved worldwide, may result in the permanent reduction in the number of infections to zero, called eradication.[8] Herd immunity created via vaccination contributed to the eventual eradication of smallpox in 1977 and has contributed to the reduction of other diseases.[9] Herd immunity applies only to contagious disease, meaning that it is transmitted from one individual to another.[7] Tetanus, for example, is infectious but not contagious, so herd immunity does not apply.[6]
Herd immunity was recognized as a naturally occurring phenomenon in the 1930s when it was observed that after a significant number of children had become immune to measles, the number of new infections temporarily decreased.[10] Mass vaccination to induce herd immunity has since become common and proved successful in preventing the spread of many infectious diseases.[11] Opposition to vaccination has posed a challenge to herd immunity, allowing preventable diseases to persist in or return to populations with inadequate vaccination rates.[12][13][14]
The exact herd immunity threshold (HIT) varies depending on the basic reproduction number of the disease. An example of a disease with a high threshold is the measles, with a HIT exceeding 95%.[15]
This is the best that I could manage . Anyone in the group is welcome to share an easier understanding of the issue and the meaning of the term HERD IMMUNITY .


Comments
Post a Comment